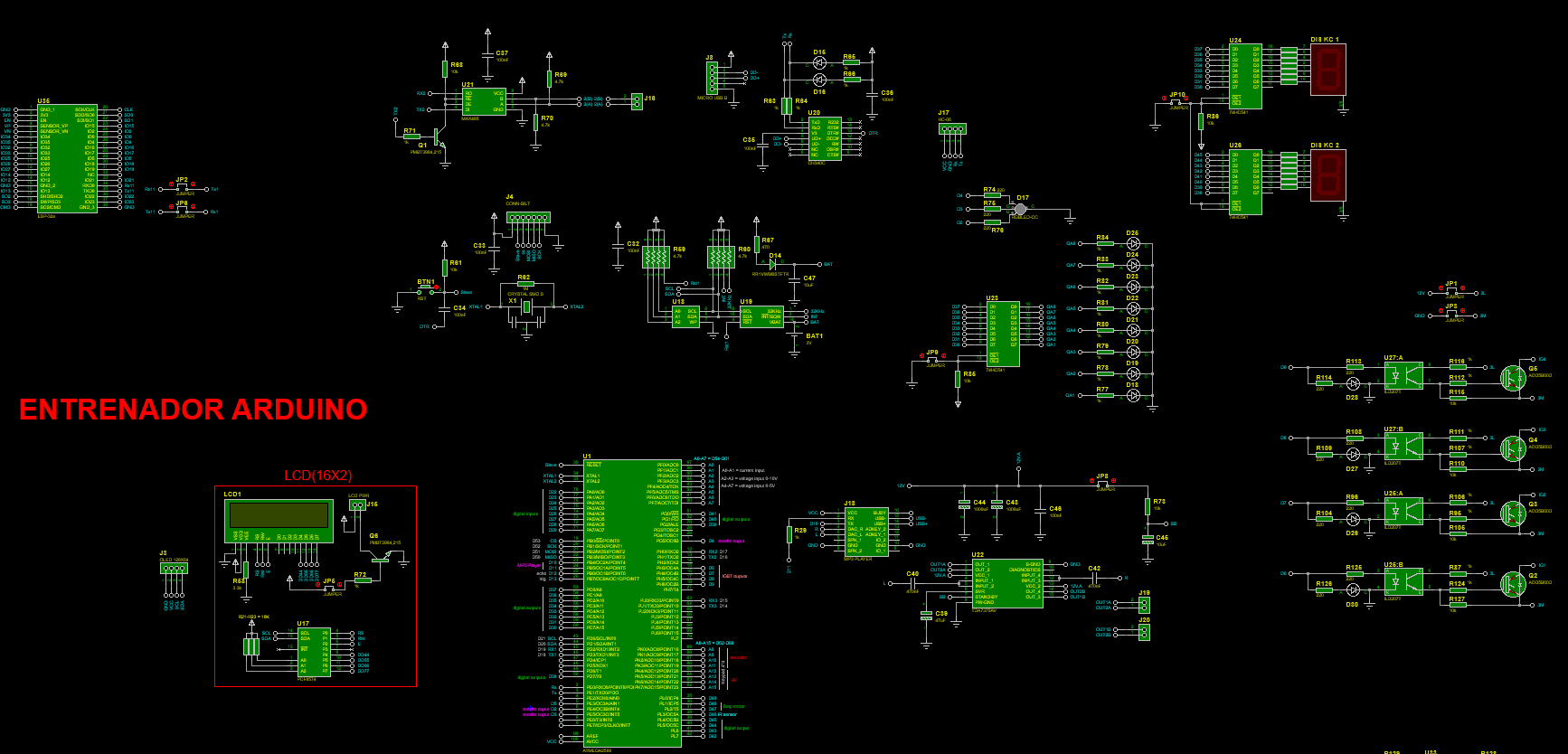
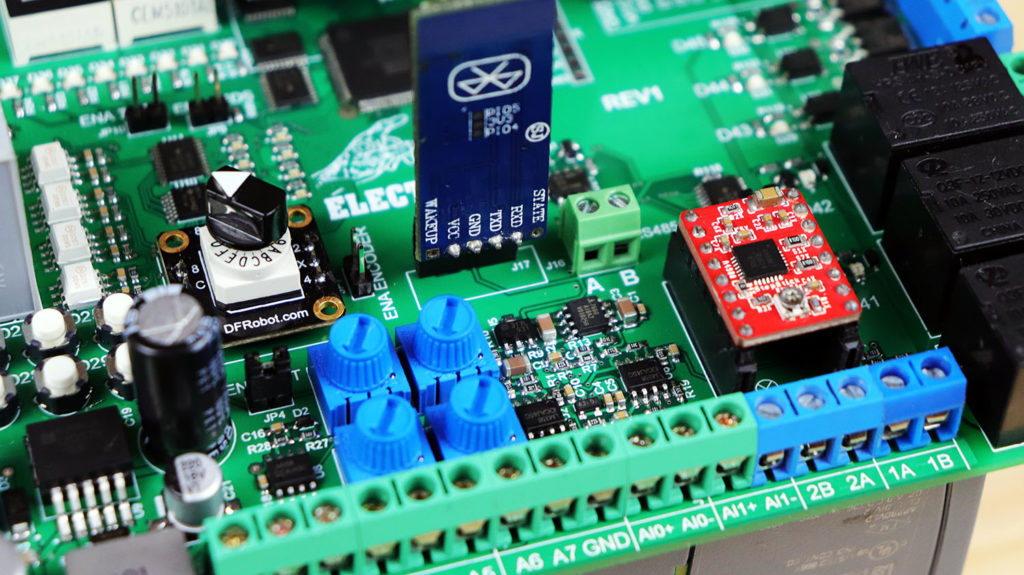
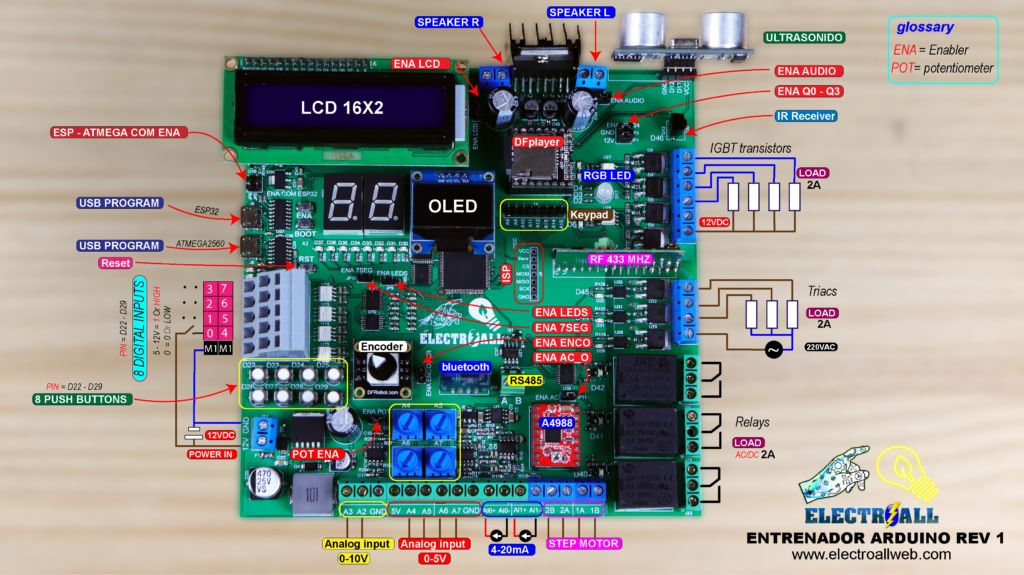
INTRODUCCIÓN
Arto de realizar conexiones cableadas cuando se requiere trabajar con las tarjetas de arduino, sensores, módulos y componentes externos? pues no te preocupes, hoy crearemos una tarjeta PCB completo que incorpore la mayoría de sensores y módulos que se trabaja con arduino, tales como; ESP32 que nos sirve para una comunicación wifi, modulo bluetooth, reloj de tiempo real, reproductor de música y su respectivo amplificador de sonido estéreo hasta 35W, pantalla LCD, pantalla OLED, entradas digitales de 5-12V con sus respectivos pulsadores, teclado matricial de 4*4, control remoto de RF de 433Mhz, sensor ultrasonido, encoder de 4bits, entradas analógicas de corriente (4-20mA), entradas analógicas de voltaje de 0-5V y de 0-10V con potenciómetro incorporado, led RGB, 8bits de leds normales, display de 7 segmentos, salidas a transistores IGBT, salidas a triac para controlar corriente alterna, salidas a relay, salida para motor paso a paso y muchas opciones más. Considero que lo más importante es poder poder subir cualquier programa de manera directa (ordenador – tarjeta entrenadora).
ESPECIFICACIONES TÉCNICAS

- Tensión de alimentación……………………….…………12VDC
- Corriente de alimentación………………….……………350mA
- Entadas digitales 5-12VDC……………………….……8
- teclado (keypad 4*4)…………………………………………..Sí
- RF 433Mhz control remoto………………………………..Sí
- IR Control remoto……………………………………………….Sí
- Sensor ultrasonido………………………………………………Sí
- Encoder (4btis)……………………………………………………..Sí
- Entradas analógicas (corriente) 4-20mA………..2
- Entradas analógicas (voltaje) 0-5V…………….…..4
- Entradas analógicas (voltaje) 0-5V “potenciometro incorporado”…………….…..4
- Entradas analógicas (voltaje) 0-10V…………..…..2
- Led RGB………………………………………1
- Leds Red………………………………………8
- Display de 7segmentos………………..2
- Salidas trasistores IGBT……………………………………4
-
- Tensión DC………………………………………………30V
- Corriente DC……………………………………………2A
-
- Salidas TRIAC………………………………………………………3
-
- Tensión AC…………..……….………………….….……250V
- Corriente AC…………………………………………….2A
-
- Salidas RLY…………………………………………………………3
-
- Tensión AC…………..……….………………….….……250V
- Corriente AC…………………………………………….2A
- Tensión DC………………………………………………30V
- Corriente DC……………………………………………2A
-
- Salida para motor paso a paso (A4988)………………..1
- Reproductor de música (DFplayer)………………………..1
- Amplificador de sonido estéreo 35W……………………1
- Pantalla LCD………………………………………………………………Sí
- Pantalla OLED……………………………………………………………Sí
- Puerto de comunicación serial para Atmega2560…………………Sí
- Puerto de comunicación serial para ESP32……………………………Sí
- Comunicación ISP……………………………………..……….1
- Comunicación I2C…………………….……….………………1
- Comunicación RS485..……………….…….………………..Sí
- ESP32 (WIFI)……………………………………………………………..Sí
- Bluetooth………………………………………………………………….Sí
- Reloj de tiempo real………………………………………..Sí
- Programación Directa………………………………………..Ordenador – Tarjeta entrenadora
- Entorno de programación………………………..………..Arduino IDE
- Condiciones ambientales min……………………….….-40°
- Condiciones ambientales max…………………..……….85°
- Dimensiones……………………………………………………….150x150mm
LISTA DE MATERIALES

| Categoría | Cantidad | Referencias | Valor | PCB Package | Datasheet |
| Condensadores | 31 | C1,C4,C5,C6,C7,C8,C10,C11,C12, C13,C14,C15,C16,C17,C18,C23, C24,C25,C26,C27,C28,C29,C30, C32,C33,C34,C35,C36,C37,C38,C41 |
100nF | 0603_CAP | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 5 | C2,C3,C9,C31,C47 | 10uF | 1206_CAP | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 3 | C19,C43,C44 | 1000uF | ELEC-RAD25 | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 1 | C20 | 470uF | CAP SMD 10.5X10MM ALUMINUM 470UF/35V | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 1 | C21 | 220uF | CAP SMD 6.3X7.7MM ALUMINUM 220UF/16V | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 2 | C22,C46 | 100nF | 1206_CAP | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 1 | C39 | 47uF | CAP SMD 5X5.4MM ALUMINUM 47UF/16V | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 2 | C40,C42 | 470nF | 0603_CAP | (see & buy) |
| Condensadores | 1 | C45 | 10uF | CAP SMD 5X5.4MM ALUMINUM 47UF/16V | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R1,R14 | 10 | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R2,R15 | 15k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R3,R16 | 51k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 30 | R4,R5,R11,R13,R17,R18,R22, R24,R30,R31,R32,R33,R34,R35,R36, R37,R38,R55,R56,R57,R61,R68, R85,R86,R118,R132,R135,R138,R142,R143 |
10k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R6,R19 | 20k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R7,R20 | 2k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 7 | R8,R21,R69,R70,R133,R136,R139 | 4.7k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 1 | R9 | 240 | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 1 | R10 | 1.8k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R12,R23 | 100 | 1206_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 34 | R25,R26,R27,R28,R29,R47,R48,R49, R50,R51,R52,R53,R54,R63,R64,R65, R66,R71,R72,R77,R78,R79,R80,R81, R82,R83,R84,R131,R134,R137, R140,R141,R144,R145 |
1k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 8 | R39,R40,R41,R42,R43,R44,R45,R46 | 10k | 1206_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 1 | R58 | 3.3k | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 2 | R59,R60 | 4.7k | RES_ARRAY 0603X4 | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 1 | R62 | 1M | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 1 | R67 | 470 | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 5 | R73,R105,R110,R115,R127 | 10k | 0805_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 31 | R74,R75,R76,R88,R89,R90,R91,R92, R93,R94,R96,R97,R98,R99,R100, R101,R102,R103,R104,R108,R109, R113,R114,R119,R120,R122,R123, R125,R126,R129,R130 |
220 | 0603_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 8 | R87,R95,R106,R107,R111, R112,R116,R124 |
1k | 0805_RES | (see & buy) |
| Resistencias | 3 | R117,R121,R128 | 470 | 0805_RES | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U1 | ATMEGA2560 | QFP50P1600X1600X120-100 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 3 | U2,U6,U8 | LM358N | SO8 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U3 | ICL7660 | SO8 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 2 | U4,U7 | TL431 | SOT23-3 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U5 | LM317L | SOT89 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U9 | LM2576-5,0 | TO170P1410X464-6 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U10 | 74HC14 | TSSOP14 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 5 | U11,U23,U24,U26,U30 | 74HC541 | TSSOP20 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U12 | IRM-3638T-X | IRM3638TX | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 6 | U13,U14,U15,U16,U25,U27 | ILD207T | SO8 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U17 | PCF8574 | SO16W | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U18 | AT24C512B | SO8 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U19 | DS3232 | SO16W | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 2 | U20,U37 | CH340C | SO16 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U21 | MAX485 | SO8 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U22 | TDA7375AV | TO127P500X2020X2210-15P | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 3 | U28,U31,U33 | TLP265J | SOIC250P670X300-4 | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 3 | U29,U32,U34 | T405Q-600 | DPAK-N | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U35 | ESP-32s | ESP-32S | (see & buy) |
| Integrados | 1 | U36 | LD1117S33 | SOT230P700X180-4 | (see & buy) |
| Transistores | 7 | Q1,Q6,Q7,Q8,Q9,Q10,Q11 | PMBT3904,215 | SOT23-3 | (see & buy) |
| Transistores | 4 | Q2,Q3,Q4,Q5 | AOD5B60D | D-PACK1 | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 2 | D1,D2 | MM3Z5V1T1G | SOD-323 | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 2 | D3,D4 | B330A-13-F | DIOM5226X230N | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 8 | D5,D6,D7,D8,D9,D10,D11,D12 | LED-GREEN | LEDC1608X60 | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 1 | D13 | SS14-TP | DIOM5226X230N | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 4 | D14,D33,D35,D37 | RR1VWM6STFTR | SOD2614X116 | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 20 | D15,D16,D18,D19,D20,D21, D22,D23,D24,D25,D26,D27, D28,D29,D30,D31,D32,D34, D36,D38 |
LED-RED | LEDC2012X120 | (see & buy) |
| Diodos | 1 | D17 | RGBLED-CC | LED RGB CC | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | BAT1 | 3V | BAT 3V | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 3 | BTN1,BTN10,BTN11 | RST | BUTTON SMD 2P | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 8 | BTN2,BTN3,BTN4,BTN5, BTN6,BTN7,BTN8,BTN9 |
BUTTON | BUTTON TH 2P | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 2 | DIS KC 1,DIS KC 2 | display 7sig | DISPLAY 7SEG | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | F1 | 1A | FUSE SMD | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 9 | J1,J2,J11,J19,J20,J27,J28,J29,J30 | TBLOCK-M2 | T-BLOCK 2PIN BLUE | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J3 | OLED 128X64 | OLED 128X64 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J4 | CONN-SIL7 | CONN-SIL7 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 6 | J5,J6,J7,J23,J24,J25 | TBLOCK-M3 | T-BLOCK 3PIN BLUE | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 2 | J8,J9 | MICRO USB B | MICRO USB B | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J10 | KFM736-5_0-5P | KFM736-5.0-5P P=5.0MM | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J12 | RF RECEIVER | RF RECEIVER | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J13 | HC-SR04 | HC-SR04 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J14 | Keypad_4*4 | ARDUINO-SIL8 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J15 | LCD PWR | LCD 16X2 PWR | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J16 | TBLOCK-M2 | TBLOCK MINI 2PIN | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J17 | HC-06 | HC-06 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J18 | MP3 PLAYER | MP3 PLAYER | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 2 | J21,J22 | TBLOCK-M3 | T-BLOCK 3PIN GREEN | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | J26 | A4988 | A4988 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 11 | JP1,JP2,JP3,JP4,JP5,JP6, JP7,JP8,JP9,JP10,JP11 |
JUMPER | CONN-SIL2 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | L1 | 100u | INDUCTOR 100UH | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | LCD1 | LM016L | LCD 16X2 | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 3 | RL1,RL2,RL3 | 12V | RL12V NORMAL | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 4 | RV1,RV2,RV3,RV4 | 1k | POTENCIOMETER MANU SMALL | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | SW1 | ENCODER DFR | ENCODER DFR | (see & buy) |
| Miscelánea | 1 | X1 | CRYSTAL SMD S | OSCILADOR SMD CERAMIC RESONATORS | (see & buy) |
COMO SUBIR BOOTLOADER

PASO 1 : SUBIR GESTOR DE ARRANQUE (BOOTLOADER)
Para poder usar un microcontrolador nuevo (atmega2560-16AU), es necesario subir un un gestor de arranque como también llamado “BOOTLOADER”, esto nos facilitará subir programas en futuras ocasiones.
finalmente para quemar el bootloader se tendrá que realizar a través de los pines ICSP, que prácticamente serían los pines [ (MOSI=PIN51) (MISO = PIN50) (SCK=PIN52) (Slave=PIN53) ]. Para subir y quemar el gestor de arranque necesitaremos un arduino UNO ó MEGA y realizar las siguientes conexiones (ARDUINO UNO – TARJETA ENTRENADORA).
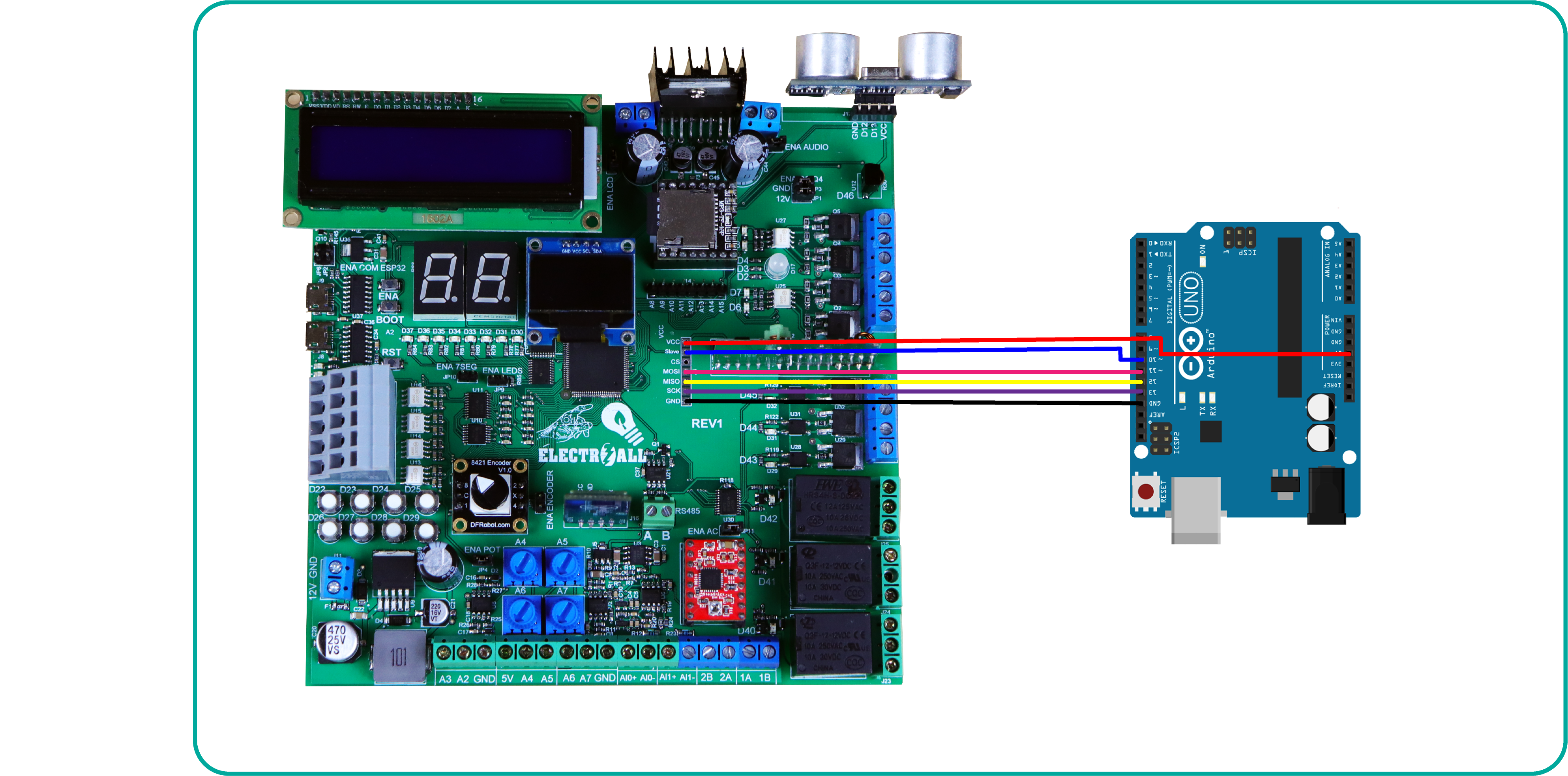
PASO 2 : SUBIR PROGRAMA; PC – TARJETA ENTRENADORA
Después de haber subido el gestor de arranque finalmente ya podremos subir cualquier programa como normalmente lo realizamos a través del puerto serie.
CODIGO DE PRUEBA

ENTRADAS DIGITALES Y SALIDAS LEDS
//TESTER DIGITAL INPUTS 12VDC
// Digital inputs
const int IN0 = 22;
const int IN1 = 23;
const int IN2 = 24;
const int IN3 = 25;
const int IN4 = 26;
const int IN5 = 27;
const int IN6 = 28;
const int IN7 = 29;
//MOSFET'S OUTPUTS
int LED0 = 30;
int LED1 = 31;
int LED2 = 32;
int LED3 = 33;
int LED4 = 34;
int LED5 = 35;
int LED6 = 36;
int LED7 = 37;
void setup() {
//DIGITAL INPUTS
pinMode(IN0, INPUT);
pinMode(IN1, INPUT);
pinMode(IN2, INPUT);
pinMode(IN3, INPUT);
pinMode(IN4, INPUT);
pinMode(IN5, INPUT);
pinMode(IN6, INPUT);
pinMode(IN7, INPUT);
//IGBT'S OUTPUTS
pinMode(LED0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED5, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED6, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED7, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(IN0) == 1)digitalWrite(LED0, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED0, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN1) == 1)digitalWrite(LED1, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED1, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN2) == 1)digitalWrite(LED2, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED2, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN3) == 1)digitalWrite(LED3, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED3, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN4) == 1)digitalWrite(LED4, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED4, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN5) == 1)digitalWrite(LED5, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED5, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN6) == 1)digitalWrite(LED6, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED6, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN7) == 1)digitalWrite(LED7, 1);
else digitalWrite(LED7, 0);
}
KEYPAD Y DISPLAY 7 SEG
int a = 37; ///////////////////////////////////////
int b = 36; ///////////////////////////////////////
int c = 35; ///////////////////////////////////////PINES PARA EL CONTADOR
int d = 34; ///////////////////////////////////////DE UNIDADES
int e = 33; ///////////////////////////////////////
int f = 32; ///////////////////////////////////////
int g = 31; ///////////////////////////////////////
int A = 45; ///////////////////////////////////////
int B = 44; ///////////////////////////////////////
int C = 43; ///////////////////////////////////////
int D = 42; ///////////////////////////////////////PINES PARA EL CONTADOR
int E = 41; ///////////////////////////////////////DE DECENAS
int F = 40; ///////////////////////////////////////
int G = 39; ///////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int dos [7] = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g}; // UNIDADES
int uno [7] = {A, B, C, D, E, F, G}; // DECENAS
//--UNIDADES--/////////////////////////////////////////
int unidad0 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}; //= #0
int unidad1 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #1
int unidad2 [7] = {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1}; //= #2
int unidad3 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; //= #3
int unidad4 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1}; //= #4
int unidad5 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #5
int unidad6 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #6
int unidad7 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #7
int unidad8 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #8
int unidad9 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #9
//--DECENAS--////////////////////////////////////////////
int decena0 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}; //= #0
int decena1 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #1
int decena2 [7] = {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1}; //= #2
int decena3 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; //= #3
int decena4 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1}; //= #4
int decena5 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #5
int decena6 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #6
int decena7 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #7
int decena8 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #8
int decena9 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #9
#include <Keypad.h>
const byte COLUMNAS = 4;
const byte FILAS = 4;
char teclas [FILAS] [COLUMNAS] = {
{'1', '2', '3', 'X'},
{'4', '5', '6', 'B'},
{'7', '8', '9', 'C'},
{'*', '0', '#', '='}
};
byte filasPines[FILAS] = {62, 63, 64, 65}; //Define lineas
byte columnasPines[COLUMNAS] = {66 , 67 , 68 , 69}; //Define columnas
Keypad miTeclado = Keypad( makeKeymap(teclas), filasPines, columnasPines, FILAS, COLUMNAS );
void setup() {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
pinMode (uno[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode (dos[i], OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
char tecla = miTeclado.getKey();
if (tecla == '0' && tecla != NO_KEY) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad0[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '1')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad1[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '2')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad2[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '3')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad3[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '4')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad4[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '5')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad5[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '6')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad6[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '7')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad7[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '8')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad8[i]);
}
}
if ((tecla == '9')) {
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad9[i]);
}
}
}
POTENCIOMETRO (ENTRADA ANALOGICA “0-5”) Y SALIDAS TRANSISTORES
// SET IQ1Q0T OTPUTS
const int Q0 = 6;
const int Q1 = 7;
const int Q2 = 8;
const int Q3 = 9;
/////////////////////////
//****POTENTIOMETEQ2 A4-A7***
void setup() {
pinMode(Q0,OUTPUT);
pinMode(Q1,OUTPUT);
pinMode(Q2,OUTPUT);
pinMode(Q3,OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int VQ0= map(analogRead(A4),0,1023,0,255);
analogWrite(Q0,VQ0);
int VQ1= map(analogRead(A5),0,1023,0,255);
analogWrite(Q1,VQ1);
int VQ2= map(analogRead(A6),0,1023,0,255);
analogWrite(Q2,VQ2);
int VQ3= map(analogRead(A7),0,1023,0,255);
analogWrite(Q3,VQ3);
}
(ENTRADA ANALOGICA “0-10”) Y SALIDAS LED RGB
// SET IQ1Q0T OTPUTS
const int B = 2;
const int G = 3;
/////////////////////////
//****INPUT (0-10V) A2-A3***
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(B, OUTPUT);
pinMode(G, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int VQ0 = map(analogRead(A3), 0, 1023, 0, 255);
analogWrite(B, VQ0);
Serial.println(analogRead(A3));
int VQ1 = map(analogRead(A2), 0, 1023, 0, 255);
analogWrite(G, VQ1);
Serial.println(analogRead(A2));
delay(1000);
}
ENTRADAS DE CORRIENTE (4-20mA), Salida led RGB
const int B = 2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
//LED BLUE OUPUTS
pinMode (B, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
//CURRENT INPUT (4-20mA) A0-A1 "4mA = 0V; 20mA = 2.7V
// VOLTAGE VALUE
int analog0 = analogRead(A1);
float voltage0 = analog0 * 0.004887585532746823069403714565;// = 5V/1023
Serial.print("voltage0 = " );
Serial.print (voltage0);
Serial.println ("V");
int pwm_out = voltage0 * 94.44444444444444; // = 255/2.70V
analogWrite(B, pwm_out);
delay(700);// Opcional
}
ENTRADAS DIGITALES Y SALIDAS TRIAC & RELAY
// SET T= TRIACS RL= RELAYS
const int T0 = 45;
const int T1 = 44;
const int T2 = 43;
const int RL0 = 42;
const int RL1 = 41;
const int RL2 = 40;
const int IN0 = 22;
const int IN1 = 23;
const int IN2 = 24;
const int IN3 = 25;
const int IN4 = 26;
const int IN5 = 27;
/////////////////////////
void setup() {
pinMode(IN0, INPUT);
pinMode(IN1, INPUT);
pinMode(IN2, INPUT);
pinMode(IN3, INPUT);
pinMode(IN4, INPUT);
pinMode(IN5, INPUT);
pinMode(T0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(T1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(T2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RL0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RL1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(RL2, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
if (digitalRead(IN0) == 1)digitalWrite(T0, 1);
else digitalWrite(T0, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN1) == 1)digitalWrite(T1, 1);
else digitalWrite(T1, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN2) == 1)digitalWrite(T2, 1);
else digitalWrite(T2, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN3) == 1)digitalWrite(RL0, 1);
else digitalWrite(RL0, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN4) == 1)digitalWrite(RL1, 1);
else digitalWrite(RL1, 0);
if (digitalRead(IN5) == 1)digitalWrite(RL2, 1);
else digitalWrite(RL2, 0);
}
ULTRASONIDO Y LCD (16X2)
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // Debe descargar la Libreria que controla el I2C
#include<Wire.h>
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
int trigger = 13; // declaramos la palabra trigger como un tipo entero y al mismo tiempo reemplaza al pin 9
int echo = 12; // declaramos la palabra echo como un tipo entero y al mismo tiempo reemplaza al pin 8
float tiempo_de_espera, distancia; // creamos una variable de fotante; es decir, nos puede dar resultados en decimales.
void setup() {
pinMode (trigger, OUTPUT); // declarmos el pin 9 como salida
pinMode (echo, INPUT); // declaramos el 8 como entrada
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.clear();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("ELECTROALL"); // Mensaje a despegar
delay(3000);
lcd.clear();
}
void loop() {
digitalWrite (trigger, LOW); // ponemos en bajo el pin 8 durante 2 microsegundos
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite (trigger, HIGH);// ahora ponemos en alto pin 8 durante 10 microsegundos;
delayMicroseconds (10); // pues este el momento en que emite el sonido durante 10 segungos
digitalWrite (trigger, LOW); // ahora ponemos en bajo pin 8
tiempo_de_espera = pulseIn (echo, HIGH); // pulseIn, recoge la señal del sonido que emite el trigger
/*La función pulseIn espera la aparición de un pulso en una entrada y mide su duración, dando como resultado la duración medida
El primer parámetro (ECHO) es el pin sobre el que se realizará la medición.
Y el segundo parámetro (HIGH) indica si el pulso a esperar será un 1 (HIGH) o un 0 (LOW).
*/
distancia = (tiempo_de_espera / 2) / 29.15; // formula para hallar la distancia
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("distancia"); // Mensaje a despegar
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(distancia); // Mensaje a despegar
lcd.setCursor(7, 1);
lcd.print("cm");
delay(3000);
lcd.clear();
}
REPRODUCTOR DE MP3 – AMPLIFICADOR SONIDO
#include "Arduino.h"
#include "SoftwareSerial.h"
#include "DFRobotDFPlayerMini.h"
//Pulsadores
const int s1 = 22; // pulsadores
const int s2 = 23;
const int led = 30; // led
int state1 = 0; // estados para las entradas digitales
int last1 = 1;
int state2 = 0;
int last2 = 1;
SoftwareSerial mySoftwareSerial(10, 11); // RX, TX
DFRobotDFPlayerMini myDFPlayer;
void printDetail(uint8_t type, int value);
void setup()
{
mySoftwareSerial.begin(9600);
Serial.begin(115200);
Serial.println();
Serial.println(F("DFRobot DFPlayer Mini Demo"));
Serial.println(F("Initializing DFPlayer ... (May take 3~5 seconds)"));
if (!myDFPlayer.begin(mySoftwareSerial)) { //Use softwareSerial to communicate with mp3.
Serial.println(F("Unable to begin:"));
Serial.println(F("1.Please recheck the connection!"));
Serial.println(F("2.Please insert the SD card!"));
while (true);
}
Serial.println(F("DFPlayer Mini online."));
myDFPlayer.setTimeOut(500); //Set serial communictaion time out 500ms
//----Set volume----
myDFPlayer.volume(20); //Set volume value (0~30).
myDFPlayer.volumeUp(); //Volume Up
myDFPlayer.volumeDown(); //Volume Down
//----Set different EQ----
myDFPlayer.EQ(DFPLAYER_EQ_NORMAL);
//----Set device we use SD as default----
myDFPlayer.outputDevice(DFPLAYER_DEVICE_SD);
pinMode(s1, INPUT);
pinMode(s2, INPUT);
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
state1 = digitalRead(s1);
state2 = digitalRead(s2);
int vol = map(analogRead(A4),0,1023, 0, 30);
myDFPlayer.volume(vol); //Set volume value (0~30).
if (state1 != last1) {
if (state1 == LOW) {
myDFPlayer.next();
Serial.print(state1);
digitalWrite(led, 1);
delay(1000);
}
}
last1 = state1;
if (state2 != last2 ) {
if (state2 == LOW) {
myDFPlayer.previous();
digitalWrite(led, 0);
delay(1000);
}
}
last2 = state2;
}
MOTOR PASO A PASO (A4988)
int pasos = 47; // usamos el pin 6 para generar pulsos (pasos)
int direc = 48; // usamos el pin 7 para la direccion (sentido horario, antihorario)
//int tiempo=1; // tiempo que dura para girar una vuelta entera
void setup() {
pinMode (pasos, OUTPUT);
pinMode (direc, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
int c_pasos;
for (c_pasos =0; c_pasos <=2000;c_pasos ++){
digitalWrite (direc,HIGH);
digitalWrite (pasos,true);
delayMicroseconds (1000);
digitalWrite (pasos,false);
delayMicroseconds (1000);
}
for (c_pasos =2000; c_pasos >=0;c_pasos --){
digitalWrite (direc,LOW);
digitalWrite (pasos,true);
delayMicroseconds (1000);
digitalWrite (pasos,false);
delayMicroseconds (1000);
}
}
BLUETOOTH
//APAGADO Y PRENDIDO DE LED BT.
//CARLONCHITOTONIC.
int led=4; //declaramos un valor entero, para luego trabajar con (led) en el resto de la estructura
int estado=0; // =de arriba
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600); //establecemos la comunicacion serial bluetooth.
pinMode(led,OUTPUT); //declaramos el pin 13 como salida
}
void loop(){
if(Serial.available()>0)// nos aseguramos que el puerto serial este habilitado.
{
estado = Serial.read(); // almacenamos los doatos
}
switch (estado){
case'A': digitalWrite(led,HIGH);
break;
case'B': digitalWrite(led,LOW);
break;
}
}
RELOJ DE TIEMPO REAL (RTC)
/*
CREADO POR :{==[=======>>>> ELECTROALL <<<<<=======]==}
INSTAGRAM : https://www.instagram.com/electroall_/
ó @electroall_
FACEBOOK : https://web.facebook.com/ELECTROALL.ELECTRONICA/?_rdc=1&_rdr
PÁGINA WEB : https://www.electroallweb.com/
YOUTUBE : https://www.youtube.com/c/ELECTROALL
________________________________________________________
{==[=======> (Testing CLOCK REAL TIME ) <=======]==}
________________________________________________________
*/
#include <Wire.h>
#include "Sodaq_DS3231.h"
#include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> // Debe descargar la Libreria que controla el I2C
LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2);
char DiaSemana[][4] = {"Dom", "Lun", "Mar", "Mie", "Jue", "Vie", "Sab" };
const int Q1 = 13 ; // salida alarma
// La linea fija la fecha, hora y dia de la semana, se debe suprimir la linea en la segunda carga
// Ejemplo 2017 diciembre 06, 22:00:00 dia 1-Lunes (0=Dom, 1=Lun, 2=Mar, 3=Mie, 4=Jue, 5=Vie, 6=Sab)
//DateTime dt(2020, 11, 20, 21, 36, 00, 1);
const int E_OT = 63; // habilitador de pines de salida reles,
void setup ()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
rtc.begin();
lcd.init();
lcd.backlight();
lcd.clear();
// La linea fija la fecha, hora y dia de la semana, se debe suprimir la linea en la segunda carga
// rtc.setDateTime(dt);
pinMode(E_OT, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(E_OT, 1);// Con bajo se habilita. Con alto se desabilita
pinMode(Q1, OUTPUT);
}
void loop ()
{
DateTime now = rtc.now();
Serial.print(now.year(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.month(), DEC);
Serial.print('/');
Serial.print(now.date(), DEC);
Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(now.hour(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.minute(), DEC);
Serial.print(':');
Serial.print(now.second(), DEC);
Serial.print(' ');
Serial.print(DiaSemana[now.dayOfWeek()]);
Serial.println();
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print(now.year(), DEC);
lcd.print('/');
lcd.print(now.month(), DEC);
lcd.print('/');
lcd.print(now.date(), DEC);
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(now.hour(), DEC);
lcd.print(':');
lcd.print(now.minute(), DEC);
lcd.print(':');
lcd.print(now.second(), DEC);
lcd.print(' ');
lcd.print(DiaSemana[now.dayOfWeek()]);
//delay(1000); // Se actualiza cada segundo
//lcd.clear();
if ((now.dayOfWeek()) == 1 && now.hour() == 21 && now.minute() == 55 && now.second() <= 30) { // MONDAY
digitalWrite(Q1, 1);
}
else {
digitalWrite(Q1, 0);
}
}
MODBUS RS485
#include <Modbusino.h>
ModbusinoSlave modbusino_slave(1);
/* Allocate a mapping of 10 values */
uint16_t tab_reg[10];
int i;
int sensorPin = A2;
int sensorValue = 0;
void setup() {
modbusino_slave.setup(115200);
pinMode(relay, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPin);
tab_reg[4] = sensorValue;
modbusino_slave.loop(tab_reg, 10);
i = i++;
}
CONTADOR DISPLAY 7 SEG
/*
CREADO POR :{==[=======>>>> ELECTROALL <<<<<=======]==}
INSTAGRAM : https://www.instagram.com/carlos_j_fuentess/
ó @carlos_j_fuentess
FACEBOOK : https://web.facebook.com/ELECTROALL.ELECTRONICA/?_rdc=1&_rdr
PÁGINA WEB : https://www.electroallweb.com/
YOUTUBE : https://www.youtube.com/c/ELECTROALL
________________________________________________________
{==[=======> (CONTADOR ) <=======]==}
________________________________________________________
*/
// no cambiar las el const int
const int pulsador_asc = 23; // ENTRADA IN1 PARA CONTAR ASCENDENTEMENTE
// ascendentes
const int pulsador_des = 22; // ENTRADA IN2 PARA CONTAR DESCENDENTEMENTE
// descendentes
//VARIABLES PARA EL CONTADOR ASCENDIENTE
// estas variables si puede ser cambiado
int contador = 0; // contador para el numero de veces presinados
int estado_pulsador_asc = 0; // estado actual del pulsador
int lastButtonState_asc = 0; // estado anterior del pulsador
//VARIABLES PARA EL CONTADOR DESCENDIENTE
// estas variables si puede ser cambiado
int estado_pulsador_des = 0; // estado actual del pulsador
int lastButtonState_des = 0; // estado anterior del pulsador
const int sir = 4;
//////////////////////////////////////////////////
int a = 37; ///////////////////////////////////////
int b = 36; ///////////////////////////////////////
int c = 35; ///////////////////////////////////////PINES PARA EL CONTADOR
int d = 34; ///////////////////////////////////////DE UNIDADES
int e = 33; ///////////////////////////////////////
int f = 32; ///////////////////////////////////////
int g = 31; ///////////////////////////////////////
int A = 45; ///////////////////////////////////////
int B = 44; ///////////////////////////////////////
int C = 43; ///////////////////////////////////////
int D = 42; ///////////////////////////////////////PINES PARA EL CONTADOR
int E = 41; ///////////////////////////////////////DE DECENAS
int F = 40; ///////////////////////////////////////
int G = 39; ///////////////////////////////////////
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////
int dos [7] = {a, b, c, d, e, f, g}; // UNIDADES
int uno [7] = {A, B, C, D, E, F, G}; // DECENAS
//--UNIDADES--/////////////////////////////////////////
int unidad0 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}; //= #0
int unidad1 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #1
int unidad2 [7] = {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1}; //= #2
int unidad3 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; //= #3
int unidad4 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1}; //= #4
int unidad5 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #5
int unidad6 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #6
int unidad7 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #7
int unidad8 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #8
int unidad9 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #9
//--DECENAS--////////////////////////////////////////////
int decena0 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0}; //= #0
int decena1 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #1
int decena2 [7] = {1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1}; //= #2
int decena3 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; //= #3
int decena4 [7] = {0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1}; //= #4
int decena5 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #5
int decena6 [7] = {1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #6
int decena7 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0}; //= #7
int decena8 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1}; //= #8
int decena9 [7] = {1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1}; //= #9
int counter = 0; //CONTADOR UNIDADES
int contadorD = 0; //CONTADOR DECENAS
int counter1 = 0; // CONTADOR PARA EL CAMBIO DE COLOR
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(pulsador_asc, INPUT); //Resistencia de pullup interna
pinMode(pulsador_des, INPUT); //Resistencia de pullup interna
pinMode(sir, OUTPUT);
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
pinMode (uno[i], OUTPUT);
pinMode (dos[i], OUTPUT);
}
}
void loop() {
// almacenamos la lectura de la entrada de pin 2
estado_pulsador_asc = digitalRead(pulsador_asc);
estado_pulsador_des = digitalRead(pulsador_des);
// comparar el estado del botón a su estado anterior
if (estado_pulsador_asc != lastButtonState_asc) {
// si el estado fue cambiado, incremente el conteo
if (estado_pulsador_asc == LOW) {
// si el estado actual es alto, entonces
// que pase de off a on:
if (counter < 99) {
contador++;
counter++;
Serial.print("CONTEO= ");
Serial.println(contador);
Serial.print("CONTEO_sis= ");
Serial.println(counter);
delay(100);
if (counter == 10 || counter == 20 || counter == 30 || counter == 40 || counter == 50 || counter == 60 || counter == 70 || counter == 80 || counter == 90) {
contadorD++;
delay(100);
}
}
}
}
lastButtonState_asc = estado_pulsador_asc;
// comparar el estado del botón a su estado anterior
if (estado_pulsador_des != lastButtonState_des ) {
// si el estado fue cambiado, decrementa el conteo
if (estado_pulsador_des == HIGH) {
// si el estado actual es alto, entonces
// que pase de off a on:
if (counter > 0 ) {
contador--;
counter--;
Serial.print("CONTEO= ");
Serial.println(contador);
Serial.print("CONTEO_sis= ");
Serial.println(counter);
delay(100);
if (counter == 9 || counter == 19 || counter == 29 || counter == 39 || counter == 49 || counter == 59 || counter == 69 || counter == 79 || counter == 89) {
contadorD--;
delay(100);
}
if (contador == -1) {
contador = 9;
}
}
}
}
//guarda el último estado actual como el ultimo estado
//para el proximo bucle
lastButtonState_des = estado_pulsador_des;
if (contador == 10) {
contador = 0;
}
switch (contador) {
case 0:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad0[i]);
}
break;
case 1:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad1[i]);
}
break;
case 2:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad2[i]);
}
break;
case 3:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad3[i]);
}
break;
case 4:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad4[i]);
}
break;
case 5:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad5[i]);
}
break;
case 6:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad6[i]);
}
break;
case 7:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad7[i]);
}
break;
case 8:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad8[i]);
}
break;
case 9:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (uno[i], unidad9[i]);
}
break;
}
switch (contadorD) {
case 0:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena0[i]);
}
break;
case 1:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena1[i]);
}
break;
case 2:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena2[i]);
}
break;
case 3:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena3[i]);
}
break;
case 4:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena4[i]);
}
break;
case 5:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena5[i]);
}
break;
case 6:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena6[i]);
}
break;
case 7:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena7[i]);
}
break;
case 8:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena8[i]);
}
break;
case 9:
for (byte i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
digitalWrite (dos[i], decena9[i]);
}
break;
}
if (counter >= 50) {
digitalWrite(sir, 1);
}
else {
digitalWrite(sir, 0);
}
}